Nursing care altered fluid balance edapt, the cornerstone of maintaining optimal health, plays a crucial role in managing fluid imbalances, ensuring patient safety, and promoting positive clinical outcomes. Understanding the signs, symptoms, and types of fluid imbalances is essential for nurses to provide effective interventions and patient education.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of nursing care for altered fluid balance, empowering nurses with the knowledge and skills to deliver exceptional patient care.
The subsequent paragraphs will explore the nursing assessment process, outlining the vital signs and symptoms to monitor. We will delve into the various types of fluid imbalances, their causes, and the rationale for each nursing intervention. Additionally, we will emphasize the significance of patient education and discuss the role of nurses in empowering patients to manage their fluid balance effectively.
Nursing Assessment: Nursing Care Altered Fluid Balance Edapt
Assessing fluid balance is a crucial aspect of nursing care, as it helps identify and manage imbalances that can have significant implications for patient health.
Signs and Symptoms of Altered Fluid Balance
- Dehydration: Dry mouth, sunken eyes, decreased skin turgor, oliguria
- Overhydration: Edema, weight gain, hypertension, pulmonary congestion
Types of Fluid Imbalances
- Dehydration: Fluid loss exceeding intake
- Hypervolemia: Excess fluid in the body
Causes of Fluid Imbalances
- Dehydration: Diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating, inadequate fluid intake
- Hypervolemia: Excessive fluid intake, renal failure, heart failure
Nursing Interventions
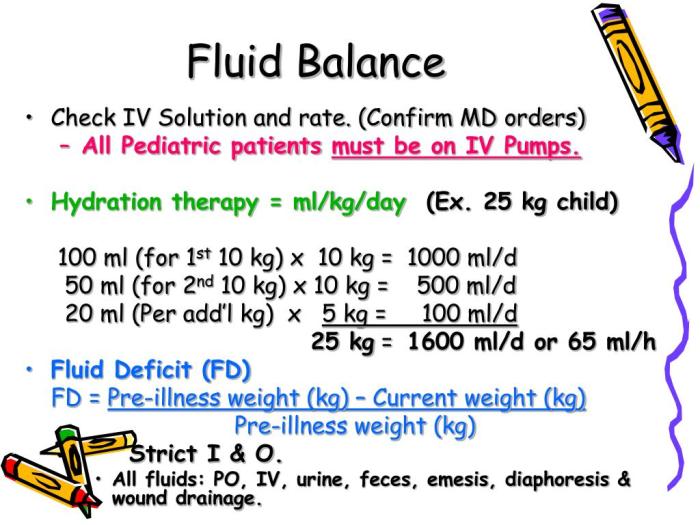
Nursing interventions for altered fluid balance aim to correct imbalances and maintain fluid homeostasis.
Examples of Nursing Interventions
- For dehydration: Administer IV fluids, encourage oral fluids, monitor intake and output
- For hypervolemia: Restrict fluids, administer diuretics, monitor weight and vital signs
Rationale for Interventions
- IV fluids: Replenish fluid deficit and correct dehydration
- Oral fluids: Encourage fluid intake to prevent dehydration
- Diuretics: Promote fluid excretion and reduce hypervolemia
Importance of Monitoring Fluid Balance, Nursing care altered fluid balance edapt
Monitoring fluid balance is essential to assess the effectiveness of interventions and detect any changes in the patient’s condition.
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Diagnoses
- Dehydration
- Hypervolemia
Goals
- Maintain fluid balance
- Prevent complications
Interventions
- Assess fluid intake and output
- Monitor vital signs
- Administer fluids as prescribed
- Encourage oral fluid intake
- Restrict fluids if necessary
Evaluation Criteria
- Stable vital signs
- Adequate fluid intake and output
- Absence of complications
Patient Education
Patient education is crucial for managing fluid balance.
Importance of Patient Education
- Empowers patients to take responsibility for their fluid intake
- Reduces the risk of complications
Examples of Patient Education Materials
- Written handouts on fluid balance
- Interactive online resources
Role of the Nurse
Nurses play a vital role in educating patients about fluid balance by:
- Assessing patient knowledge
- Providing clear and concise information
- Answering patient questions
Case Study
Assessment
A 65-year-old male with a history of heart failure presents with edema, weight gain, and shortness of breath.
Interventions
- Restricted fluids
- Administered diuretics
- Monitored weight and vital signs
Outcomes
The patient’s edema and weight gain improved significantly. His shortness of breath also subsided.
Analysis
The nursing interventions were effective in correcting the patient’s fluid imbalance and improving his symptoms.
Detailed FAQs
What are the common signs and symptoms of altered fluid balance?
Altered fluid balance can manifest in various ways, including changes in urine output, skin turgor, mucous membranes, and vital signs. Dehydration may present with decreased urine output, dry skin and mucous membranes, and tachycardia, while hypervolemia can lead to increased urine output, edema, and hypertension.
How do nurses assess fluid balance?
Nursing assessment involves monitoring fluid intake and output, assessing skin turgor and mucous membranes, and measuring vital signs. Nurses also consider the patient’s medical history, medications, and underlying conditions that may impact fluid balance.
What are the different types of fluid imbalances?
Fluid imbalances can be classified into two main categories: dehydration and hypervolemia. Dehydration occurs when there is a deficit of fluids, while hypervolemia is characterized by an excess of fluids.
How do nurses intervene to correct fluid imbalances?
Nursing interventions for altered fluid balance aim to restore and maintain fluid balance. Interventions may include administering fluids intravenously or orally, restricting fluids, or administering diuretics to promote fluid excretion.
Why is patient education important in managing fluid balance?
Patient education is crucial for empowering patients to manage their fluid balance effectively. Nurses provide education on the importance of maintaining adequate hydration, recognizing signs and symptoms of fluid imbalances, and adhering to prescribed fluid intake recommendations.