Apex fitness club uses straight-line depreciation – Apex Fitness Club’s adoption of straight-line depreciation, a fundamental accounting method, has shaped its financial reporting and decision-making. This article delves into the intricacies of straight-line depreciation, its implications for Apex Fitness Club, and its advantages and disadvantages in comparison to alternative depreciation methods.
Straight-line depreciation is a systematic allocation of an asset’s cost over its useful life, resulting in equal depreciation expenses throughout the asset’s lifespan. This method provides a consistent and predictable approach to depreciation, ensuring a stable expense pattern on the income statement and a gradual reduction in the asset’s book value on the balance sheet.
1. Straight-Line Depreciation
Straight-line depreciation is a method of allocating the cost of a capital asset evenly over its useful life. This method assumes that the asset will lose value at a constant rate over time.
To calculate straight-line depreciation, the following formula is used:
Depreciation Expense = (Cost of Asset
Residual Value) / Useful Life
For example, if an asset costs $10,000, has a residual value of $1,000, and has a useful life of 5 years, the annual depreciation expense would be $1,800.
Advantages of Straight-Line Depreciation
- Simple and easy to calculate.
- Results in a consistent depreciation expense over the asset’s useful life.
- Matches the expected pattern of asset use.
Disadvantages of Straight-Line Depreciation
- Does not reflect the declining value of an asset over time.
- May result in overstating the asset’s value in the early years of its useful life.
- May result in understating the asset’s value in the later years of its useful life.
2. Apex Fitness Club
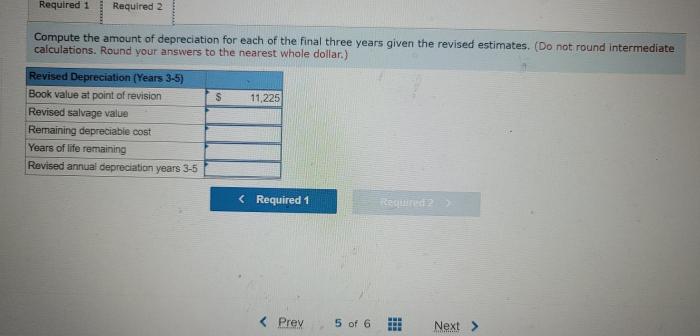
Apex Fitness Club is a chain of fitness centers that operates in the United States. The company has over 100 locations and offers a variety of fitness classes and equipment to its members.
Apex Fitness Club chose to use straight-line depreciation for its capital assets because it is a simple and straightforward method that results in a consistent depreciation expense over the asset’s useful life. This method also matches the expected pattern of asset use, as the fitness equipment is used evenly throughout its useful life.
Potential Impact of Straight-Line Depreciation on Apex Fitness Club’s Financial Statements
- Reduces the carrying value of capital assets over time.
- Increases depreciation expense in the early years of an asset’s useful life.
- Decreases depreciation expense in the later years of an asset’s useful life.
3. Comparison to Other Depreciation Methods
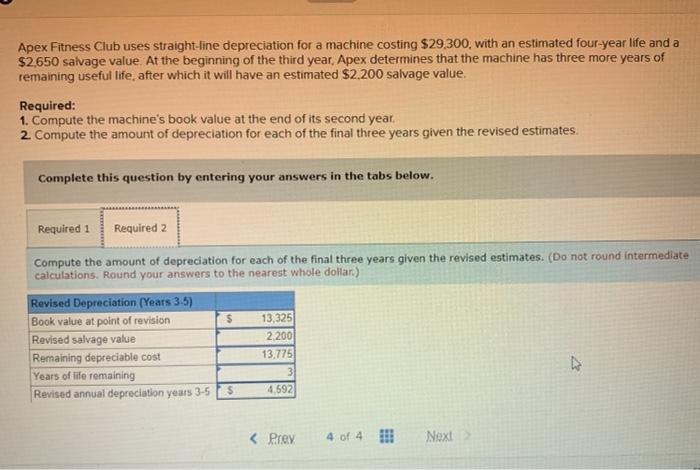
Straight-line depreciation is one of several methods that can be used to depreciate capital assets. Other common methods include double-declining balance depreciation and sum-of-the-years’-digits depreciation.
Double-declining balance depreciation accelerates depreciation in the early years of an asset’s useful life, while sum-of-the-years’-digits depreciation allocates more depreciation to the early years of an asset’s useful life than to the later years.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Straight-line depreciation | Simple and easy to calculate. | Does not reflect the declining value of an asset over time. |
| Double-declining balance depreciation | Accelerates depreciation in the early years of an asset’s useful life. | Can result in a higher depreciation expense in the early years of an asset’s useful life than is actually justified. |
| Sum-of-the-years’-digits depreciation | Allocates more depreciation to the early years of an asset’s useful life than to the later years. | Can result in a higher depreciation expense in the early years of an asset’s useful life than is actually justified. |
4. Accounting Implications
Straight-line depreciation has several accounting implications. First, it reduces the carrying value of capital assets over time. This is because the depreciation expense is recorded as a reduction to the asset’s book value.
Second, straight-line depreciation increases depreciation expense in the early years of an asset’s useful life. This is because the depreciation expense is calculated as a percentage of the asset’s cost, and the asset’s cost is highest in the early years of its useful life.
Third, straight-line depreciation decreases depreciation expense in the later years of an asset’s useful life. This is because the depreciation expense is calculated as a percentage of the asset’s cost, and the asset’s cost is lowest in the later years of its useful life.
Example of Recording a Straight-Line Depreciation Expense, Apex fitness club uses straight-line depreciation
To record a straight-line depreciation expense, the following journal entry is used:
Depreciation Expense xxAccumulated Depreciation xx
5. Tax Implications: Apex Fitness Club Uses Straight-line Depreciation
Straight-line depreciation also has several tax implications. First, it reduces taxable income. This is because depreciation expense is a deductible expense for tax purposes.
Second, straight-line depreciation can affect the timing of taxes. This is because depreciation expense is deducted over the asset’s useful life, rather than all at once. This can result in a lower tax liability in the early years of an asset’s useful life and a higher tax liability in the later years of an asset’s useful life.
Example of Calculating the Tax Savings Associated with Straight-Line Depreciation
To calculate the tax savings associated with straight-line depreciation, the following formula is used:
Tax Savings = Depreciation Expense
Tax Rate
For example, if an asset has a depreciation expense of $1,000 and the tax rate is 25%, the tax savings would be $250.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the formula for calculating straight-line depreciation?
Depreciation Expense = (Asset Cost – Residual Value) / Useful Life
What are the advantages of using straight-line depreciation?
– Simplicity and ease of calculation – Consistent and predictable depreciation expenses – Tax benefits due to even distribution of depreciation over the asset’s life
What are the disadvantages of using straight-line depreciation?
– May not accurately reflect the asset’s declining value over time – Can result in overstated asset values in the later years of the asset’s life