Transcription and translation biology worksheet answers – Unveiling the intricacies of transcription and translation, this worksheet delves into the fundamental processes that govern the flow of genetic information. Through engaging explanations, diagrams, and thought-provoking questions, we explore the molecular mechanisms underlying gene expression and its regulation, providing a comprehensive understanding of these critical biological processes.
This guide empowers students with a solid foundation in transcription and translation, equipping them to navigate complex biological concepts with confidence.
Transcription Process

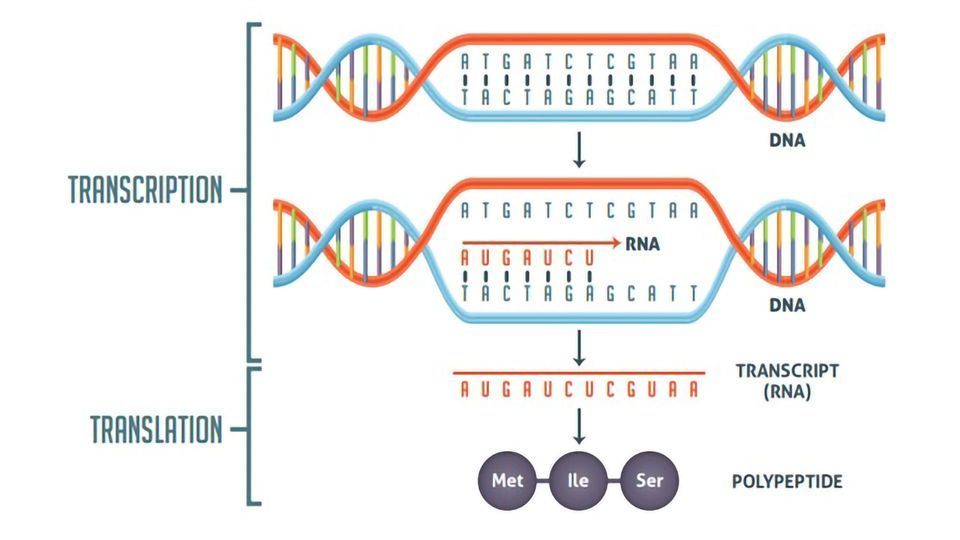
Transcription is the process by which DNA is copied into RNA. It is carried out by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. RNA polymerase binds to a specific region of DNA called the promoter. It then unwinds the DNA and synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule.
The RNA molecule is then released from the DNA template and can be used to produce proteins.

Role of RNA Polymerase in Transcription
RNA polymerase is the enzyme that carries out transcription. It is a complex enzyme that consists of several subunits. The core subunits of RNA polymerase are responsible for binding to DNA and synthesizing RNA. Other subunits of RNA polymerase help to regulate the transcription process.
Translation Process

Translation is the process by which RNA is used to produce proteins. It is carried out by a complex called a ribosome. Ribosomes bind to mRNA and read the codons in the mRNA. Each codon codes for a specific amino acid.
The ribosome then uses the amino acids to synthesize a protein.

Role of Ribosomes in Translation
Ribosomes are the structures that carry out translation. Ribosomes are composed of two subunits: a large subunit and a small subunit. The large subunit of the ribosome binds to mRNA and reads the codons. The small subunit of the ribosome binds to tRNA and brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome.
Transcription and Translation Regulation
The transcription and translation processes are tightly regulated. This regulation ensures that the cell produces the proteins it needs when it needs them.
Factors that Regulate Transcription and Translation
There are a number of factors that can regulate transcription and translation. These factors include:
- Transcription factors
- MicroRNAs
- Environmental factors
Role of Transcription Factors in Regulating Gene Expression
Transcription factors are proteins that bind to DNA and regulate the transcription of genes. Transcription factors can either activate or repress transcription. Activators bind to DNA and promote the transcription of genes. Repressors bind to DNA and block the transcription of genes.
Role of MicroRNAs in Regulating Gene Expression
MicroRNAs are small RNAs that regulate the translation of genes. MicroRNAs bind to mRNA and prevent it from being translated. This can lead to decreased production of the protein encoded by the mRNA.
Transcription and Translation Errors
Transcription and translation are complex processes that are prone to errors. These errors can lead to the production of non-functional proteins.
Types of Errors that Can Occur During Transcription and Translation
There are a number of different types of errors that can occur during transcription and translation. These errors include:
- Point mutations
- Insertions
- Deletions
- Frameshifts
Consequences of Transcription and Translation Errors
Transcription and translation errors can have a number of different consequences. These consequences include:
- Production of non-functional proteins
- Cell death
- Cancer
Mechanisms that Cells Use to Correct Transcription and Translation Errors
Cells have a number of different mechanisms to correct transcription and translation errors. These mechanisms include:
- Proofreading
- Repair enzymes
- Nonsense-mediated decay
Applications of Transcription and Translation: Transcription And Translation Biology Worksheet Answers
Transcription and translation are essential processes for life. They are used to produce the proteins that are needed for all cellular functions.
Applications of Transcription and Translation in Biotechnology
Transcription and translation are used in a variety of biotechnology applications. These applications include:
- Production of proteins for medical research
- Genetic engineering
- Biofuel production
Production of Proteins for Medical Research
Transcription and translation are used to produce proteins for medical research. These proteins can be used to study the function of genes and to develop new drugs.
Genetic Engineering
Transcription and translation are used in genetic engineering to produce organisms with new traits. These organisms can be used to improve crop yields, to produce new medicines, and to clean up environmental pollution.
Biofuel Production, Transcription and translation biology worksheet answers
Transcription and translation are used in biofuel production to produce fuels from renewable resources. These fuels can be used to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
Helpful Answers
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA molecules using a DNA template. It unwinds the DNA double helix, reads the sequence of nucleotide bases, and assembles a complementary RNA molecule.
How do ribosomes contribute to translation?
Ribosomes are complex molecular machines that decode the genetic information carried by mRNA molecules. They bind to mRNA and tRNA molecules, facilitate the formation of peptide bonds, and synthesize proteins according to the genetic code.
What are the potential consequences of transcription and translation errors?
Errors during transcription and translation can lead to the production of non-functional or harmful proteins. These errors can contribute to genetic disorders, developmental abnormalities, and various diseases.