The urinary system nephron coloring exercise embarks on a captivating journey into the intricate world of renal physiology. Through an interactive and engaging approach, this exercise provides a comprehensive understanding of the urinary system’s anatomy, physiology, and clinical applications.
Delving into the structural intricacies of the nephron, the functional unit of the kidney, learners will gain insights into its vital role in filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. The exercise empowers students to visualize and comprehend the complex processes involved in urine formation.
Anatomy of the Urinary System
The urinary system is a complex network of organs that work together to filter waste products from the blood and excrete them from the body. The main organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Kidneys
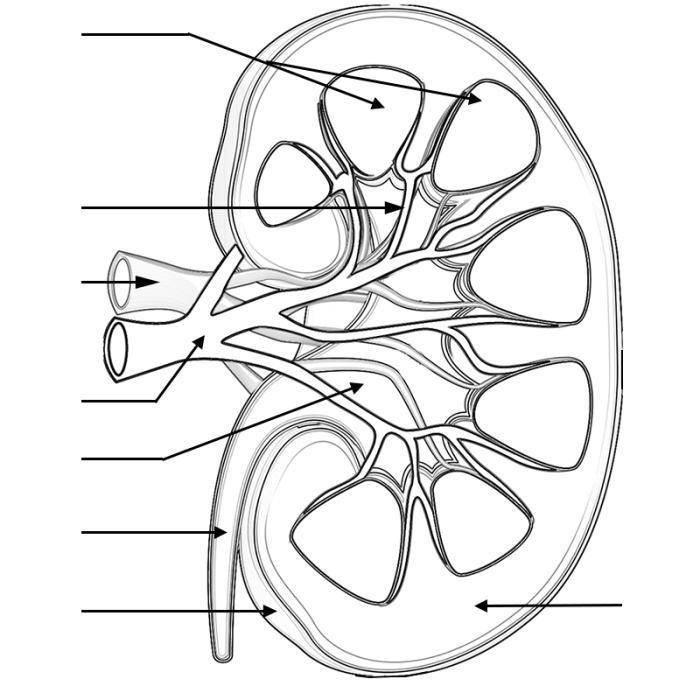
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine, just below the rib cage. They are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. The kidneys are made up of millions of tiny filtering units called nephrons.
Ureters
The ureters are two thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The ureters are lined with smooth muscle that helps to propel urine downward.
Bladder
The bladder is a muscular organ that stores urine until it is released through the urethra. The bladder is lined with a waterproof membrane that prevents urine from leaking out.
Urethra
The urethra is a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The urethra is lined with a waterproof membrane that prevents urine from leaking out.
Structure of the Nephron
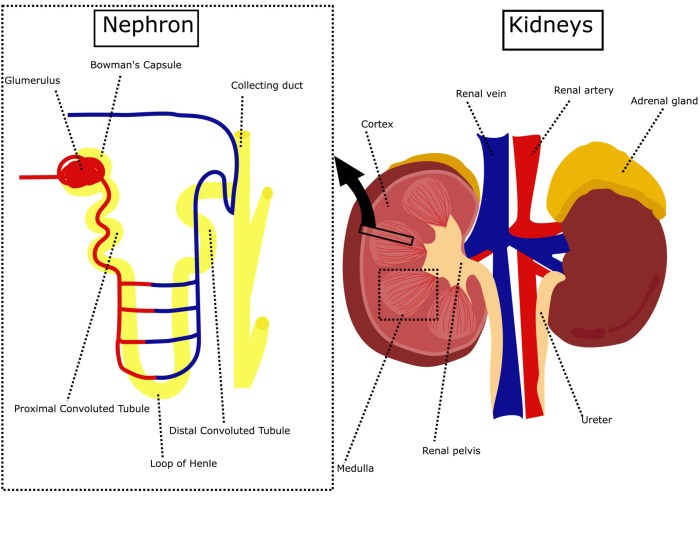
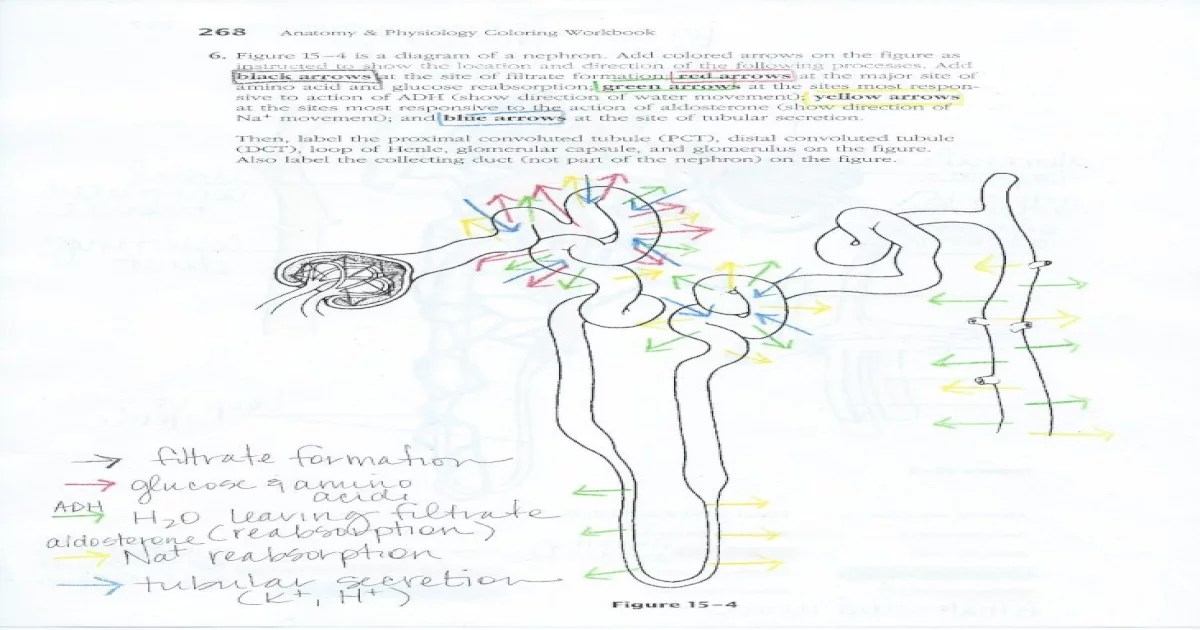
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. Each kidney contains about 1 million nephrons. The nephron is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine.
Glomerulus
The glomerulus is a network of tiny blood vessels located in the Bowman’s capsule. The glomerulus is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood.
Bowman’s Capsule
The Bowman’s capsule is a cup-shaped structure that surrounds the glomerulus. The Bowman’s capsule collects the filtrate from the glomerulus.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule, Urinary system nephron coloring exercise
The proximal convoluted tubule is a long, coiled tube that leads away from the Bowman’s capsule. The proximal convoluted tubule reabsorbs water, glucose, and other nutrients from the filtrate.
Loop of Henle
The loop of Henle is a U-shaped tube that leads away from the proximal convoluted tubule. The loop of Henle helps to concentrate the filtrate by reabsorbing water and sodium.
Distal Convoluted Tubule
The distal convoluted tubule is a long, coiled tube that leads away from the loop of Henle. The distal convoluted tubule reabsorbs more water and sodium from the filtrate.
Collecting Duct
The collecting duct is a tube that collects urine from the distal convoluted tubules. The collecting duct carries the urine to the renal pelvis, which is the funnel-shaped structure that leads to the ureter.
User Queries: Urinary System Nephron Coloring Exercise
What is the purpose of the nephron?
The nephron is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood, reabsorbing essential nutrients, and secreting hormones that regulate various bodily functions.
How does the nephron contribute to urine formation?
The nephron plays a crucial role in urine formation through the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus, where blood is filtered to remove waste products. Reabsorption takes place in the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule, where essential nutrients and water are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream.
Secretion involves the active transport of certain substances from the bloodstream into the nephron.