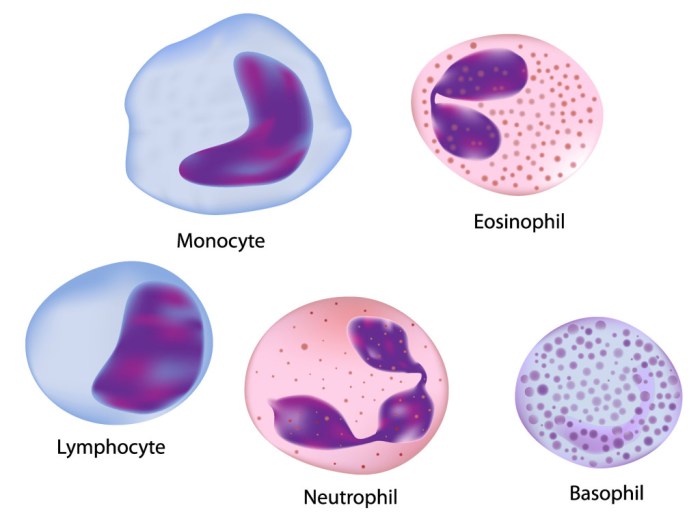
Four leukocytes are diagrammed in figure 10 2 – Four leukocytes are diagrammed in Figure 10.2, providing a comprehensive visual representation of these essential immune cells. This figure serves as a valuable tool for understanding their distinct morphologies, functions, and clinical significance.
The four leukocytes depicted in the figure include neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and eosinophils. Each type possesses unique morphological features and characteristics that enable them to perform specialized roles in the immune system.
Overview of Figure 10.2: Four Leukocytes Are Diagrammed In Figure 10 2
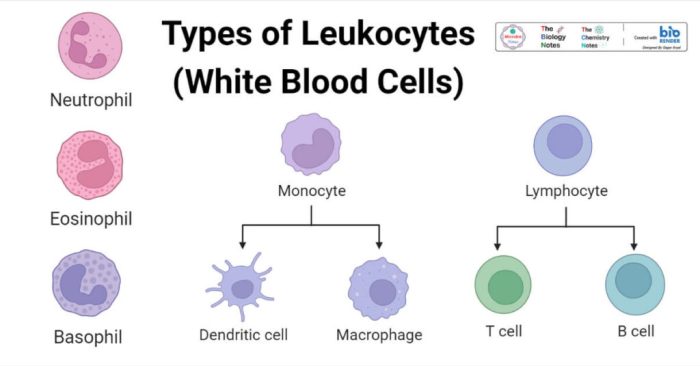
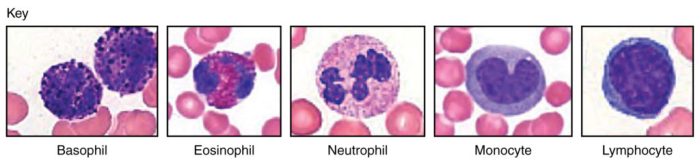
Figure 10.2 is a diagram depicting four types of leukocytes, which are essential components of the immune system. These cells play crucial roles in defending the body against pathogens, infections, and foreign substances.
The four leukocytes featured in the figure are neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and lymphocytes. Each type possesses distinct morphological characteristics and functions, contributing to the overall immune response of the body.
Detailed Examination of Leukocytes
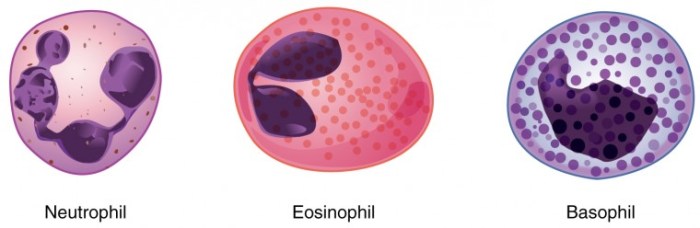
- Neutrophils:The most abundant type of leukocyte, neutrophils are characterized by their multi-lobed nucleus and pale cytoplasm. They are the first responders to infections, phagocytosing and destroying pathogens.
- Eosinophils:Eosinophils are larger than neutrophils and have a bilobed nucleus. They are involved in defense against parasitic infections and allergic reactions.
- Basophils:Basophils are the least common type of leukocyte and have a U- or S-shaped nucleus. They release histamine and other inflammatory mediators, contributing to allergic reactions and inflammation.
- Lymphocytes:Lymphocytes include T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells. They are responsible for adaptive immunity, recognizing and eliminating specific pathogens and cancer cells.
Functional Comparison of Leukocytes
The four leukocytes have distinct functions that contribute to the overall immune response:
- Neutrophils:Phagocytosis of pathogens, release of antimicrobial substances
- Eosinophils:Defense against parasites, release of cytotoxic substances
- Basophils:Release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators
- Lymphocytes:Antigen recognition, antibody production, cell-mediated immunity
Clinical Significance of Leukocytes, Four leukocytes are diagrammed in figure 10 2
Leukocyte counts and morphology are important indicators of overall health and immune function:
- Elevated neutrophil counts may indicate bacterial infections.
- Increased eosinophil counts may suggest parasitic infections or allergies.
- Reduced lymphocyte counts can indicate immunosuppression or HIV infection.
- Abnormal leukocyte morphology may be associated with leukemia or other blood disorders.
Query Resolution
What are the four types of leukocytes shown in Figure 10.2?
Neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and eosinophils.
What is the primary function of neutrophils?
Phagocytosis and destruction of bacteria.
How do lymphocytes contribute to the immune response?
They produce antibodies and recognize and destroy infected cells.